Polystorm - Geocellular Water Management System
Polystorm is an efficient and versatile geocellular water management system for Sustainable urban Drainage Systems (SuDS) compliant attenuation, det

In the arid regions of the Middle East, water is vital for sustaining life. The way we manage water across industries, including construction, is crucial in creating thriving urban environments that support health and wellbeing.
Sustainable urban Drainage Systems (SuDS) have become increasingly prominent in recent years, and for good reason. Almost every development needs a drainage system in place to function effectively. The task is finding how to take that development from simply functional, to also environmentally beneficial.
That’s where SuDS come in.
What are SuDS?
SuDS mimic the Earth’s natural water cycle to capture, store, treat and reuse water. This approach is cyclic and focuses on reuse, differentiating itself from conventionally linear systems in which water is treated as a waste product. Rather than water running directly into sewage systems, which can cause them to overflow during extreme weather, SuDS harvest water as close to where it falls as possible through a source control strategy. The surface runoff is then collected into underground networks where sediments are filtered out. This water can then be reused for irrigation and other sustainable applications.
The key is using water in a way that meets current social, economic, and ecological needs, without compromising the ability of future generations to meet those same needs. This is the principle that lies at the heart of sustainable water management.
How are SuDS different from conventional drainage systems?
Conventional drainage systems use collectors, impermeable surfaces, sewers and treatment plants as a way of managing stormwater. These systems are often not the most efficient neither from an environmental point of view, nor in terms of alleviating flood risk. The use of impermeable materials such as concrete in conventional drainage causes runoff to be rapidly transported downstream. The high peak flows generated as a consequence, risk the collapse of the sewerage infrastructures.
The source control strategy utilised by SuDS prevents this issue through attenuation rather than relying on diversion of runoff. Through replicating natural processes, SuDS have a much lower impact on the surrounding environment.
The concrete typically used in conventional systems tend to be chosen for its perceived strength and durability. SuDS often use plastic as a cost-effective solution that maintains the same level of resilience, but with faster installation times. Polypipe’s polypropylene tanks typically weigh up to 94% less than their concrete equivalents, resulting in a much lower carbon footprint due to more efficient transportation and logistics.
Why are SuDS important?
Here are 4 main reasons why SuDS should be considered as an essential component of your development:
Improve Stormwater Runoff to Reduce Flood Risk
In the natural water cycle, water that infiltrates the Earth is naturally filtered through the soil, which removes toxins and sediments. In an urban environment, this is hindered by the impermeable city streets, pavements, rooftops and parking lots made of concrete. This results in higher volumes of surface runoff. The overwhelming amount of water entering drainage systems in such a short space of time causes them to overflow and flood.
SuDS mitigates flood risk through attenuation - the process of storing stormwater in geocellular cells, to be re-used when required. This alleviates stress on the drainage system by allowing water to percolate back into the ground, with the potential to reduce flood risk by 80%.
Protect Natural Systems
Surface run-off plays a significant role in local water pollution by picking up waste substances and pollutants as it flows. These are then carried into local waterways, eventually making their way into the ocean and harming ecosystems and surrounding wildlife.
SuDS feature a filtration system that removes any pollutants, ensuring the collected water is safe for reuse and diverted away from waterways.
Enhance Green Urbanisation
SuDS deliver multifunctional benefits that help reduce the impact of climate change. SuDS methods such as wetlands and open spaces help to reduce carbon and reduce the Urban Heat Island effect within cities. Collecting and reusing water in the creation of green-blue roofs also helps in this sense, thus minimising the need for air conditioning. The right SuDS solutions help to enhance urban design and planning.
Increase in Property Value and Housing Sale-ability
SuDS are not only more cost-effective than traditional drainage systems upon installation, but also offer more long-term economic benefits. The reuse of captured water reduces overall water consumption. The implementation of green roofs using SuDS, also has the potential to increase property values by up to 20%, particularly if commercialised or transformed into communal spaces.
What are the different types of SuDS and their uses?
These solutions replicate natural processes and restore, as far as possible, the hydrological cycle. There are a variety of different SuDS options that are available to developers, all of which have different uses, as well as different locations in relation to the development, or typical rainfall landing area.
There are three main distinctions for the types of SuDS available: at source, site-control, and regional control.
As previously mentioned, an at-source strategy controls water runoff at, or next to, where the rainfall lands on a surface. These are more likely what you’ll be looking for if your project is residential.
Site-controlled SuDS cover the entire development site and tend to include larger scale methods mixed with the smaller scale products. They include:
Detention basins: a depression covered with vegetation to hold rainfall and slowly drain it.
Retention ponds: a larger depression which stores water, even during dry conditions.
Wetlands: a vegetative area with shallow ponds and marshland.
Swale: shallow, vegetated channels used to store and convey runoff.
Permeable paving: ground structures that allow water to run through it or along grooves in the surface.
Filter drains: strips of ground where runoff can soak away into temporary storage.
Regional controlled SuDS can cover multiple developments within an area and tend to be on a much larger scale, draining to a particular body of water. These include three of the site-controlled tactics: detention basins, retention ponds, and wetlands.
One of the most sustainable techniques in the SuDS hierarchy are green-blue roofs. Roofing can account for up to 50% of impermeable surfaces in urban areas. Converting these unused spaces into green and green-blue roofs can significantly reduce runoff volumes. The water is instead collected and stored in plants and the surrounding growing medium, to be gradually released back into the atmosphere through evapotranspiration.
Our multi-award winning Permavoid does just that. Permavoid is best suited for shallow applications and support the creation of green-blue roofs. It can be easily integrated into the roof structure underneath the growing medium. Green-blue roofs can deliver a range of health, wellbeing, commercial and social benefits. Learn more about such benefits of green roofs here.
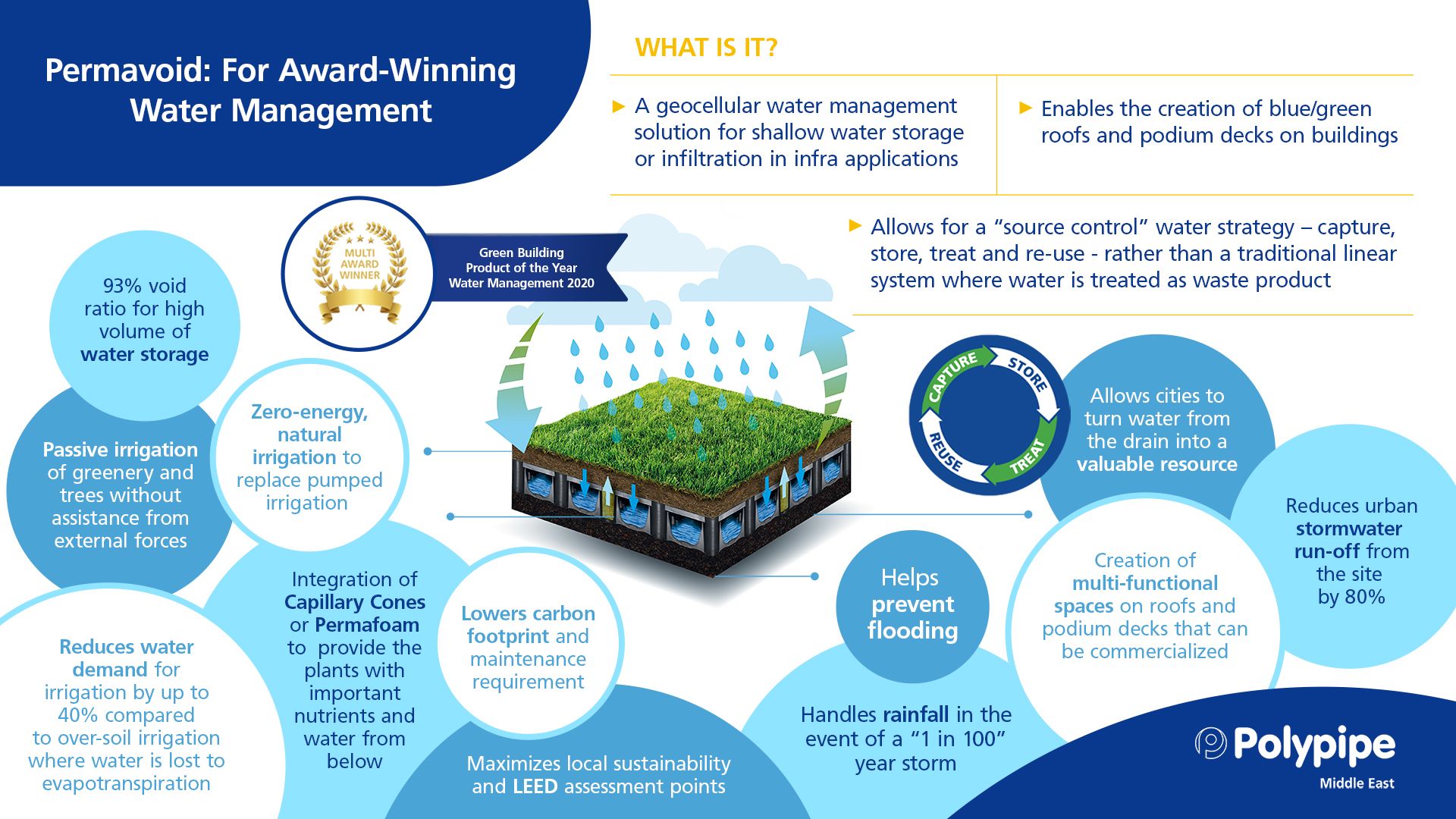
Another SuDS solution that can be implemented into urban environments and contribute to green urbanisation is Polystorm. Each Polystorm cell has a 95% void ratio for maximum water capture and retention. This is crucial for areas that are considered to be vulnerable to floods since more stormwater can be detained within a given area.
The high strength and modular nature of Polystorm systems make them suitable for source control systems where large attenuation, detention, and infiltration systems are required. This geocellular range is suitable for use beneath both trafficked and non-trafficked surfaces. It removes the need for traditional long drainage networks, as well as reduces the strain on systems already in place.
Whether you’re planning a small residential development, or a giant multi-use project, you should consider SuDS to be more than just a drainage strategy. It’s an essential component in your design.
Contact us today about the SuDS options for your development. Our SuDS design team can help you to better understand all your options and work with you to create a solution that solves all your water drainage needs.
Tel: +971 (0) 4 518 3000
Email: middleeast@polypipe.com
Polystorm is an efficient and versatile geocellular water management system for Sustainable urban Drainage Systems (SuDS) compliant attenuation, det
Permavoid is a shallow geocellular water management system aimed at managing stormwater and surface water at source, as close to where it falls as pos